
Though the World is full of uncertainties caused by tariff tensions and deepening geo-political conflicts, India’s economic fundamentals are performing robust supported by strong growth of GDP in Q4 2024-25, FDI at three years high, exports at all time high, inflation at seven years low, GST collections at all time high and steady performance of the stock markets. Going ahead, India’s economy is expected to remain strong in the current financial year too supported by anticipated good monsoon, rural demand and enhanced credit availability to the consumers and producers.
India’s last quarter Q4 2024-25 GDP grew at 7.4%, making overall GDP at 6.5% despite the severe global headwinds. In the post covid years, the GDP growth is consistently high growth, making an average of more than 7.5% during the last four years. Just after the pandemic year of covid -19 (2020-21), the GDP grew at 9.7% in 2021-22, 7.6% in 2022-23, 9.2% in 2023-24, and 6.5% in 2024-25. According to the various estimates, the GDP is expected to grow around 6.5% in the current financial year (2025-26).
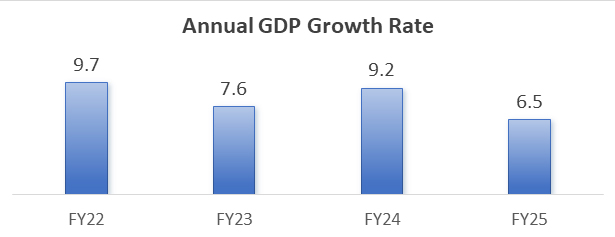
Source : Compiled from MOSPI, Government of India
In the financial year 2024-25, the growth major components grew robust, the construction sector grew at 9.4%, public admin and defense service at 8.9%, Financial, realty Services is 7.2%, Private final consumption Expenditure is 7.2%, Gross Fixed Capital Formation 7.1%, Trade Hotel is 6.1%, Utilities is 5.9%, Manufacture at 4.5%, agriculture sector at 3.5%, mining at 2.7% and government final consumption expenditure is 2.3%. The high growth of the agriculture, construction, PFCE and GFCF indicate that the demand trajectory in the country will continue. The employment scenario is also expected to improve as agriculture and construction sectors are the largest sectors of employment and absorb major chunk of workforce in the country.
The size of the Economy increased from Rs 301.22 Lakh crore (USD 3.6 Trillion) in 2023-24 to Rs330.68 Lakh crore (USD 3.9 Trillion) in 2024-25 and expected to be Rs367 Lakh crore (USD 4.1 Trillion) in 2025-26.
| S.No | Sector | GDP Growth Rate FY 2025 | Q4 FY 2025 Performance |
| 1 | Construction | 9.4 | 10.8 |
| 2 | Public Admin and Defence Services | 8.9 | 8.7 |
| 3 | Financial, realty Services | 7.2 | 7.8 |
| 4 | Private final consumption Expenditure | 7.2 | 6 |
| 5 | Gross Fixes Capital formation | 7.1 | 9.4 |
| 6 | Trade, Hotels | 6.1 | 6 |
| 7 | Utilities | 5.9 | 5.4 |
| 8 | Agriculture | 4.6 | 5.4 |
| 9 | Manufacturing | 4.5 | 4.8 |
| 10 | Mining | 2.7 | 2.5 |
| 11 | Government Final Consumption Expenditure | 2.3 | -1.8 |
Source : Compiled from MOSPI, Government of India
In the investment scenario, FDI in 2024-25 went up at three years high at USD 81 billion, and the capital market remained robust. Though the geo-political conflicts are worsening, the investment scenario vis-a-vis strong flows in capital markets remain strong. Inflation conditions are also becoming benign, May 2025 CPI softened to 2.8% and WPI to 0.39%, making further scope for repo rate cut tough the RBI has already reduced the repo rate to 5.5% in June 2025. The benign inflation conditions and reduced repo rate are expected to further boost the domestic demand and overall activity in the country.
At the Export front, India's exports are making new highs every year in the post-COVID years, went up at all time high at USD 824 billion in 2024-25. Despite troubles in red sea and disruptions in supply chain, India’s exports grew 6% in 2024-25 from USD 778 billion in 2023-24 to USD 824 billion in 2024-25. India’s merchandise and services exports in 2024-25 are valued at USD 437 billion and USD 387 billion respectively. According to FIEO (The Federation of India Export Organisation, India’s exports are also expected to touch USD 1000 billion in the current financial year 2025-26 of which value of the Merchandise exports would be USD 525-535 billion and value of services exports would be USD 465-475 billion.
The macro fundamentals so far
| S. No. | Indicators | Performance |
| 1 | GDP (2024-25) | 6.5% despite severe global headwinds |
| 2 | Projections for 2025-25 | 6.3-6.5% |
| 3 | Size of the GDP | USD 4.18 trillion |
| 4 | Total Exports (2024-25) | All-time high at USD 824 billion Merchandise USD 437 billion Services USD 387 billion |
| 5 | Projections for exports in 2025-26 (FIEO) | USD 1000 billion Merchandise USD 525-535 Services USD 465-475 |
| 6 | FDI (2024-25) | Three years high at USD 81 billion |
| 7 | CPI Inflation | May 2025 CPI softened to 2.8% |
| 8 | CPI projection in 2025-26 (average) | 3.7% |
| 9 | WPI Inflation | May WPI Inflation at 0.39% |
| 10 | Repo rate | Repo Rate Cut to 5.5% |
Source : Compiled from various sources
A softening headline inflation trajectory, robust rural demand vis-a-vis strong agricultural growth, are expected to support manufacturing sector activity in the current financial year 2025-26. The continued reforms process by the Government for MSMEs will further support the growth trajectory of the MSMEs and their contribution in the manufacturing sector and employment creation in the country.
The government focus on the ease of doing business initiatives, reducing cost of doing business such as costs of finances, costs of compliances, costs of logistics and ongoing reforms in socio-economic segments will further strengthen India’s economic resilience and competitiveness in the global marketplace.
At the global front, according to the IMF, among the top 10 leading economies, 6 economies will grow less than 2% (average) in the next six years (2025-2030), however, India to remain fastest growing economy among the top ten economies, growing at 6.5% (average) during the 2025-2030 followed by China at 3.8%, Brazil 2.9% and USA at 2.1%. India has significantly surpassed the economic growth rates of China in the post pandemic years on the back of bold economic reforms undertaken by the government.
Despite the global economic uncertainties, India grows fastest among the leading economies.
| Country | 2025 | 2026 | 2027 | 2028 | 2029 | 2030 |
| USA | 1.82 | 1.74 | 1.98 | 2.12 | 2.12 | 2.12 |
| China | 3.95 | 3.95 | 4.21 | 4.05 | 3.69 | 3.37 |
| Germany | -0.05 | 0.92 | 1.45 | 1.20 | 0.95 | 0.69 |
| India | 6.19 | 6.26 | 6.47 | 6.48 | 6.49 | 6.49 |
| Japan | 0.55 | 0.57 | 0.62 | 0.58 | 0.52 | 0.53 |
| United Kingdom | 1.07 | 1.40 | 1.53 | 1.45 | 1.44 | 1.43 |
| France | 0.64 | 1.01 | 1.18 | 1.25 | 1.20 | 1.21 |
| Italy | 0.44 | 0.83 | 0.56 | 0.68 | 0.7 | 0.7 |
| Canada | 1.37 | 1.55 | 1.71 | 1.57 | 1.64 | 1.51 |
| Brazil | 2.01 | 1.98 | 2.19 | 2.30 | 2.43 | 2.48 |
Source : Compiled from IMF
India to Surpass Germany in 2028
According to the World Economic Outlook of the IMF released in April 2024, India has surpassed Japan in the size of GDP and surpass Germany in 2028 with a GDP size of USD 5584 as compared with the size of Germany at USD 5251 billion in 2028. India will be the third largest economy in 2028 with a size of more than USD 5 trillion
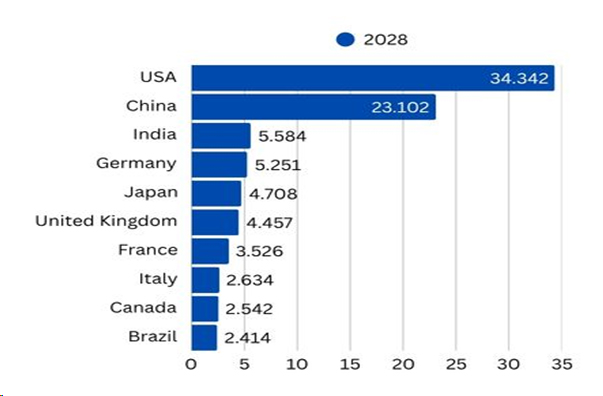
Source, World Economic Outlook, IMF
In conclusions, continued process of economic reforms in India would further strengthen the economic fundamentals of the country to maintain strong economic growth trajectory. Strengthening of India’s connectivity with Global Value Chains (GVCs) will help to improve supply chains further and reduce costs of doing business and enhanced competitiveness of the economy in the global markets and that will attract more and more domestic and foreign investments and support to create more employment opportunities for the growing young population in the country.
(Dr. S.P. Sharma is Chief Economist & Director of Research • PHDCCI (PHD Chamber of Commerce and industry, India)
Disclaimer: The opinions expressed in this article are the personal opinions of the author. The facts and opinions appearing in the article do not reflect the views of Indiastat and Indiastat does not assume any responsibility or liability for the same.
"Inclusive AI Needs Open Data, Subsidised Computing and Governance"... Read more